When we use smartphones, watch TV, operate computers, or navigate cars daily, we seldom consider the technological marvels behind these screens. Thin, vibrant, and responsive displays have become an indispensable part of our digital lives. Among these display technologies, Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Displays (TFT LCD) have dominated the consumer electronics industry for over two decades as the most widely adopted display technology. This article will delve into TFT LCD technology from multiple perspectives, revealing the underlying logic and evolutionary path of this foundational technology that profoundly impacts modern life.
TFT LCD, or Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display, is an active matrix liquid crystal display technology. Its core innovation lies in equipping each pixel with an independent thin-film transistor as a control switch, enabling precise and rapid control of every pixel.
Fundamentally, TFT LCD technology integrates advancements from multiple fields of physics and materials science:
Optical properties of liquid crystals: Liquid crystal material has unique birefringence property, and its molecular arrangement direction can be controlled by electric field, thus changing the polarization state of light.
Thin-film transistor technology:Each pixel corresponds to a micro crystal made of amorphous silicon or poly crystalline silicon.The body switch forms an active matrix, allowing pixels to retain their state without continuous refresh.
Polarized light control:The light transmittance of each sub-pixel is controlled through the coordinated work of the polarizer, liquid crystal layer and color filter.
When a specific pixel needs to be activated, the corresponding TFT switch turns on, applying voltage to the liquid crystal cell to alter the alignment of liquid crystal molecules and adjust light transmission. By precisely controlling the combination of transmittance for red, green, and blue sub-pixels, the desired colors and brightness are ultimately achieved.
Within the expansive display technology family, TFT LCD represents a pivotal branch of flat-panel displays. Compared to early cathode ray tubes (CRTs), it offers advantages such as slimness, low power consumption, and absence of geometric distortion. When measured against contemporaneous plasma displays (PDPs), it demonstrates superior performance in resolution, manufacturing cost, and lifespan. In contrast to the emerging organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), TFT LCD maintains competitive edges in cost, longevity, and large-size production.
In terms of market applications, TFT LCD spans the full spectrum from micro smartwatch screens to large outdoor billboards, forming a complete product portfolio. According to data from market research firm DSCC, TFT LCD still accounts for over 70% of global display panel shipments, making it the undisputed mainstream display technology.
Global Display Panel Technology Shipment Share Chart (Based on DSCC Report)
Display technology type | 2023 Estimated Cargo share |
Key application areas |
Brief description of the cu-rrent market situation |
TFT LCD |
~71% |
Television, monitor, laptop, tablet, in-car display, commercial The industry displays | Absolute market mainstay. With a mature industrial chain, extremely high cost-effectiveness, and irreplaceable manufacturing advantages in the field of ultra large size, we will continue to dominate the market. |
Flexible/Rigid OLED |
~28% |
Smartphones (mainly high-end), smartwatches, high-end TVs, laptops | Leader in the high-end market. The high penetration rate in the smartphone field and active expansion into the mid size IT field are the main driving forces for growth. |
Other Technologies |
~1% |
Professional display, emerging applications | Niche and future markets. Including Micro LED, quantum dot self luminous (QLED), electronic paper (E Ink), etc. At present, the market share is small, but it represents a long-term technological direction. |
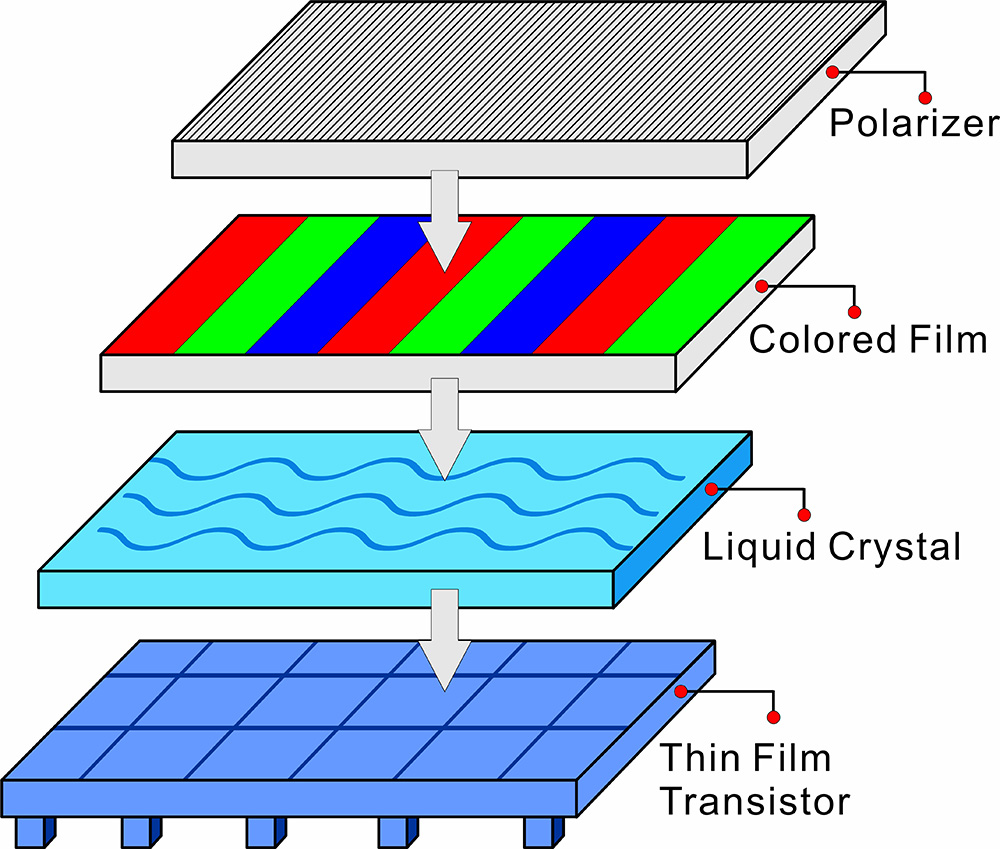
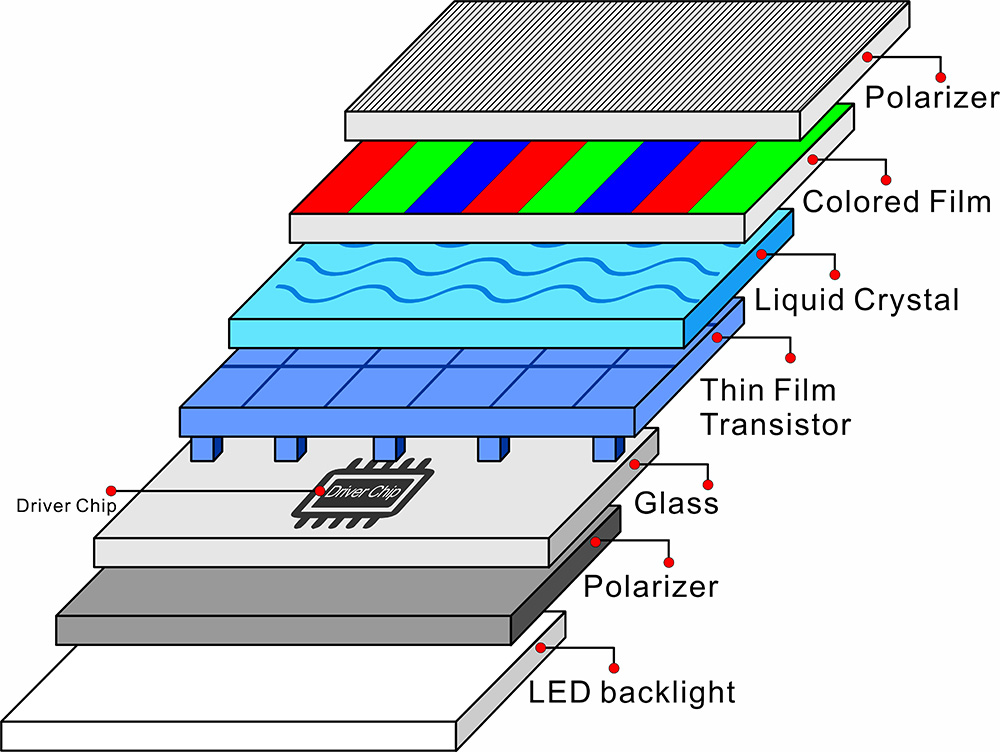
A complete TFT LCD module is formed by the precise stacking of multiple functional layers:
Backlight unit (Backlight Unit): Provides a uniform surface light source. In the early days, CCFL cold cathode fluorescent lamps were used, and modern LED arrays are mainly used.
Polarizer: The two outermost layers of polarizer, which allow only light in a specific direction to pass through.
Glass substrate :It is usually composed of two ultra-thin glass sheets, carrying a TFT array and a color filter.
TFT array layer:A thin film transistor matrix manufactured on a bottom glass substrate, with each pixel corresponding to at least one transistor.
Liquid crystal layer:The liquid crystal material sealed between two glass substrates has a thickness of only a few micrometers.
Color filter layer: The red, green and blue filter arrays are fabricated on the top glass substrate.
Drive circuit:The system incorporates source and gate drivers that convert video signals into voltage signals for pixel control.
The design of this multi-layer structure embodies the perfect integration of materials science, semiconductor technology, and optical engineering, with each layer having its specific physical function, working together to achieve high-quality image display.
Schematic diagram of the hierarchical structure of TFT LCD
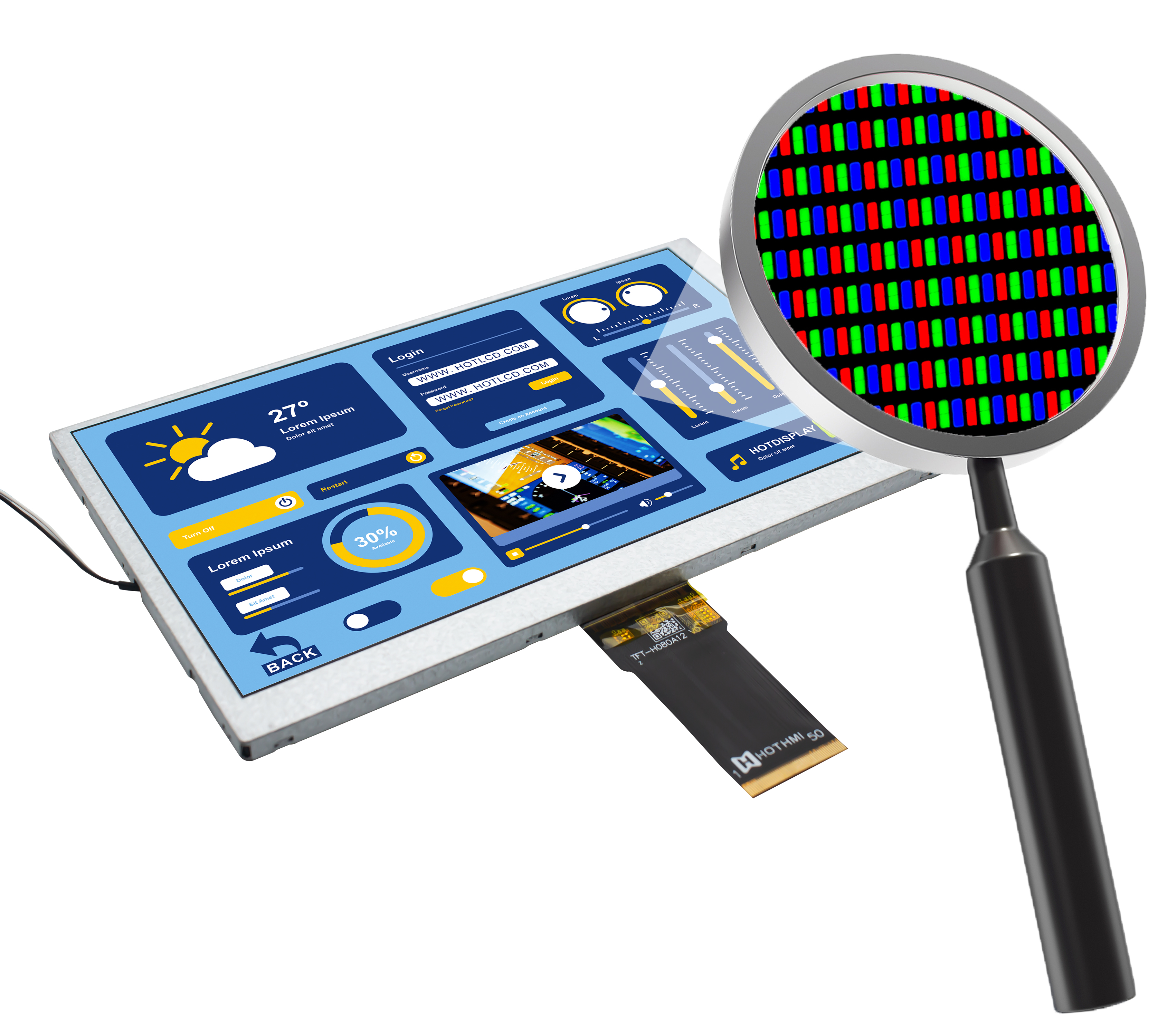
Microscopic Level: Pixel-level Engineering
At the micro scale, each TFTLCD pixel is a precise micro-elector-mechanical system. A typical pixel structure includes:
TFT switch:As the gatekeeper of pixels, it controls whether voltage is applied to the liquid crystal cell.
Liquid crystal capacitor (CLC): Stores charge and maintains the deflection state of liquid crystal molecules.
Storage capacitor:Auxiliary CLC holds charge to prevent voltage from dropping too fast.
Pixel electrode:The electric field is formed with the common electrode to drive the liquid crystal molecules to deflect.
The pixel density of modern high-resolution displays has reached astonishing levels. For example, a 6-inch smartphone screen may contain over 2 million pixels, each consisting of three sub pixels, requiring over 6 million thin-film transistors for independent control. This precise manufacturing at the microscale represents the pinnacle of modern manufacturing.

TFT LCD technology didn't emerge overnight, but rather evolved through continuous innovation and refinement.
material innovation
Liquid crystal material:From TN (twisted nematic type) to IPS (planar conversion type) and then to VA (vertical orientation type), the viewing angle and contrast continue to improve.
Semiconductor materials:From amorphous silicon (a-Si) to low-temperature poly crystalline silicon (LTPS), the electron mobility has increased by over a hundred times.
Backlight technology:The color gamut has been continuously expanding, from CCFL to white LED, and further enhanced by quantum dots.
The following table summarizes the three core technologies that have dominated the development of TFTLCD backlight, elaborating on their principles, advantages and disadvantages, and contemporary significance.
Feature dimension |
First generation: CCFL backlight |
Second generation: White LED backlight |
Third generation: Quantum dot backlight |
Core technology | Cold cathode fluorescent tube. By using high pressure to excite mercury vapor and generate ultraviolet light, the fluorescent powder on the inner wall of the lamp tube is excited to emit white light. | Blue light-emitting diodes excite yellow fluorescent powder, which mixes to produce white light. It is a basic light source that is either side in or direct down. | Photo-luminescent quantum dots. Excite quantum dot films/tubes with blue LEDs to produce pure red green light, which is then combined with the remaining blue light to produce white light. |
Core strengths | Mature technology, low initial cost, and good uniformity of luminescence. | 1. Thinner: The side in design makes the TV/monitor extremely slim. 2.Energy saving: Power consumption is 30% -50% lower than CCFL. 3.Environmental Protection: Mercury free, easier to recycle. 4. Long lifespan and high stability. | 1.Color gamut revolution: The NTSC/sRGB color gamut coverage has increased from~70% to over 100%, perfectly covering the DCI-P3 movie grade color gamut. 2. Pure color: narrow spectrum, high and accurate color saturation. 3. High brightness and efficiency. |
Main disadvantages | 1.Containing mercury, not environmentally friendly. 2.High power consumption. 3. The thick lamp tube limits the thinning of the screen. 4.Narrow color gamut (approximately NTSC72%). 5.The uniformity of brightness decreases over time. | 1. Limited color gamut improvement: Compared to CCFL, it has improved, but still cannot cover wide color gamut standards. 2. Contrast dependent structure: Side entry is difficult to achieve fine partition dimming. | 1.High cost: The material and manufacturing process costs are higher than ordinary white LED. 2.Lifespan and stability: In the early days, quantum dot materials were sensitive to oxygen and water, requiring precise packaging, but this has been greatly improved. |
Application Era and Positioning | The absolute mainstream from the 2000s to the early 2010s, widely used in early LCD TVs and displays. | The absolute mainstream since the 2010s has completely replaced CCFL and become the standard configuration for all consumer LCD products. | High end/image quality flagship positioning since 2015. Widely used in high-end televisions, professional displays, and gaming displays, it is a key technology for improving LCD image quality to compete with OLED. |
Enhance user experience | The popularization of LCD has been achieved, but the color expression (especially red and green) is relatively plain. | Bringing about a revolution in lightweight industrial design and significantly reducing energy consumption, it is the cornerstone of the popularization of LCD technology. | Bringing a disruptive color experience, LCD is able to present extremely bright, vivid, and accurate colors for the first time, with a visual impact comparable to OLED. |
Structural innovation
Self-aligning technology:Reduce the number of lithography steps and improve the production efficiency and yield.
COA technology:The color filter is directly fabricated on the TFT array to improve the aperture ratio and brightness.
GOA technology:The gate driver is integrated on the glass substrate to reduce the width of the external chip and the frame.
Process innovation
Advances in lithography technology:The area of a single processing has increased more than 50 times from the 1st generation line (300×400mm glass substrate) to the 10.5th generation line (2940× 3370mm).
Low temperature process:The use of thinner and cheaper plastic substrates is allowed to promote the development of flexible displays.
Inkjet printing technology:Revolutionary manufacturing methods that dramatically reduce material and energy consumption.
Mature industrial chain:After decades of development, a complete global supply chain has been formed, and the manufacturing cost has been continuously reduced.
High reliability:It has high technical stability and a life span of more than 50,000 hours.
Easy to mass produce: It is especially suitable for manufacturing large-size panels with obvious cost advantage.
Good visibility:IPS technology delivers wide viewing angles and precise color reproduction.
Environmental suitability:It has a wide operating temperature range and is suitable for various application environments.
Contrast limit: The backlight's constant illumination makes achieving true black impossible.
Response speed: The physical rotation of liquid crystal molecules takes time, which may cause trailing in fast motion picture.
Perspective dependence: While technologies such as IPS improve viewing angles, color and brightness still vary with viewing angles.
Thickness limitations: The backlight module and multiple functional layers are required, making it difficult to achieve an ultra-thin design.
The widespread adoption of TFT LCD technology has profoundly transformed multiple industries:
Consumer electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, TVs, etc.
Show professional: Medical displays, industrial control panels, and avionics.
Automotive electronics:The vehicle information entertainment system, digital instrument panel, head-up display.
Public display: Digital signage, information kiosks, and advertising displays.
Emerging applications:Smart home control panel, Internet of things terminal, wearable devices.
Notably, the widespread adoption of TFT LCD has directly accelerated the democratization of information. As display costs continue to drop, vast populati- ons in developing countries can now access information terminals at affordable prices, enabling them to connect to the global information network. This societal impact transcends the technical significance of the technology itself.
While competing with emerging display technologies like OLED and Micro LED, TFT LCD has not stagnated but has evolved through a series of key technological advancements.
Mini-LED backlight technology: thousands of tiny LEDs as a backlight source, achieving OLED comparable contrast and local dimming.
High refresh rate technology: The refresh rate is increased to 240Hz or even 360 Hz to meet the needs of esports and professional applications.
Low power innovation: Use new LCD mode, low power drive technology, extend the battery life of mobile devices.
Seamless integration: Touch sensor, fingerprint recognition, and camera are directly integrated into the display module.
The table below systematically outlines its core response strategies and technological upgrades:
Evolutionary dimension | Core technologies/strategies | Competitive challenges to address | Achieved effects and advantages | Typical Applications/Markets |
1.Improved image quality | Mini-LED backlight | OLED's pixel-level light control and ultra-high contrast | Upgrading traditional dozens of backlight LEDs to thousands to tens of thousands of micron-level Mini-LEDs, combined with fine local dimming, achieves an ultra-high contrast ratio of one million to one, comparable to OLED, and a higher peak brightness (>2000 nits), while eliminating the risk of screen burn-in. | High-end TVs, professional monitors, gaming monitors |
Quantum dot technology | OLED's wide color gamut and high color purity | By employing quantum dot film or QD-OLED architecture (blue OLED + QD film), the color gamut is elevated to a level surpassing OLED (such as BT.2020 85%+), resulting in more vivid and accurate colors. | Flagship TVs, high-end monitors | |
2.Performance and functionality enhancements | High refresh rate and fast LCD | OLED's extremely fast response time (e-sports, gaming) | The refresh rate has been increased to 240Hz, 360Hz or even 500Hz, and fast liquid crystal materials such as IPS Black and Fast IPS have been developed to significantly reduce gray-to-gray response time, eliminate ghosting, and meet the needs of top e-sports. | esports monitors, gaming laptops |
Low power consumption and variable refresh rate | OLED's power consumption advantage in mobile devices | Employing a new backlight design, low-power driver IC, and LTPO TFT backplane technology, it achieves a dynamic refresh rate (1Hz-120Hz), significantly extending battery life. | High-end tablets and laptops | |
3.Form innovation | Ultra-thin and narrow bezel design | The thin and flexible form of OLED | Through COF/COP packaging and a more precise structural design, the bezel is reduced to almost borderless (<1mm), achieving an extremely thin and light body. | Full-screen TVs, high-end monitors |
4.Cost and economies of scale | Generation line upgrade and process optimization | The high cost of Micro LED | We will continue to expand the production capacity of our G10.5/11 generation lines, and further reduce the cost of large-size panels through economies of scale and process improvements (such as photoorientation and inkjet printing), thereby consolidating our price advantage in mainstream markets such as televisions. | Large-screen TVs, public display screens |
5.Integration and intelligence | Embedded technology and multi-functional integration | The trend of integration of emerging technologies | By integrating touch, fingerprint recognition, ambient light sensor, camera and other features directly into the panel (In-Cell), a simpler and more reliable all-in-one design is achieved. | Smart car cockpit, all-in-one computer, Internet of Things devices |
In summary, TFT LCD's evolutionary strategy in the face of challenges can be summarized as: matching or even surpassing in picture quality, dominating in cost and scale, innovating flexibly in form, and achieving deep integration in functionality. This ensures its continued role as an unshakable cornerstone in the display industry for the foreseeable future.
The evolution of TFT LCD epitomizes modern technological progress: from fundamental scientific discoveries to laboratory prototypes, industrial applications, and continuous refinement. It represents not only the convergence of materials science, semiconductor technology, and optical engineering, but also a model of global industrial collaboration. Despite the constant emergence of new technologies, TFT LCD has demonstrated through persistent innovation that mature technologies retain remarkable vitality and evolutionary potential.
For the foreseeable future, TFT LCDs will remain the primary interface connecting us to the digital world, delivering information, sharing knowledge, and enhancing experiences. More than just a technological product, they exemplify humanity's ability to transform fundamental science into practical tools—a testament to human ingenuity that merits our deep understanding and sustained attention from multiple perspectives.
When we gaze at the display before us, we see not just images and text, but a microscopic universe that embodies decades of scientific wisdom, global industrial collaboration, and continuous technological innovation—this is TFT LCD, the silent cornerstone of modern visual technology.
With over 20 years of expertise in the LCD industry, HOTHMI delivers professional TFT LCD solutions while striving to be your long-term technical partner. We share industry insights and co-create value with you. Facing challenges in technical compatibility or cost control when choosing TFT LCD? Our 20-year industry focus enables us to provide precise recommenda- tions, ensuring the optimal balance between performance and value.